- Home
- About Us
- Courses
- NSHM Business School
- BBA (Bachelor of Business Administration)
- BBA – Hospital Management
- BBA – Global Business
- BBA – Sports Management
- BBA – Accountancy, Taxation & Auditing
- BBA – Accountancy, Taxation and Auditing + BSE Certification
- BBA – Banking & Financial Services
- MBA (Master of Business Administration)
- Executive MBA
- MHA (Master of Hospital Administration)
- NSHM Institute of Health Sciences
- Bachelor of Pharmacy
- Bachelor of Pharmacy (Lateral)
- Bachelor of Optometry
- B.Sc. – Psychology
- B.Sc. – Dietetics and Nutrition
- B.Sc. – Medical Lab Technology
- B.Sc. – Radiology & Medical Imaging Technology
- B.Sc. – Critical Care Technology
- B.Sc. – Yoga
- Master of Optometry
- Master of Optometry (BL)
- Master of Pharmacy – Pharmacology
- Master of Pharmacy – Pharmaceutics
- Master of Public Health
- Master of Public Health (BL)
- M.Sc. – Clinical Psychology
- M.Sc. – Dietetics and Nutrition
- M.Sc. – Medical Lab Technology
- M.Sc. – Radiology & Imaging Technology
- M.Sc. – Yoga
- M.Sc. – Yoga (BL)
- NSHM Design School
- NSHM Institute of Computing & Analytics
- NSHM Institute of Engineering & Technology
- B. Tech. – Mechanical Engineering
- B. Tech. – Mechanical Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. in Civil Engineering
- B. Tech. – Civil Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Computer Science Engineering
- B. Tech. – Computer Science Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Electronics & Communication Engineering
- B. Tech. – Electronics & Communication Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- B. Tech. – Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Electrical Engineering
- B. Tech. – Electrical Engineering (Lateral)
- B. Tech. – Data Science
- B. Tech. – Data Science (Lateral)
- NSHM Institute of Hotel & Tourism Management
- BBA – Aviation Hospitality Services and Management
- BBA – Travel & Tourism Management
- B.Sc. – Culinary Science
- Bachelor of Hotel Management & Catering Technology
- B.Sc. – Hospitality & Hotel Administration
- Master of Tourism & Travel Management
- Master of Tourism & Travel Management (BL)
- M.Sc. – Hospitality Management
- M.Sc. – Hospitality Management (BL)
- NSHM Institute of Nursing
- NSHM Media School
- NSHM Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology
- NSHM Business School
- Schools & Campuses
- Beyond Academics
- Admissions
- News & Events
- Contact Us
Overview
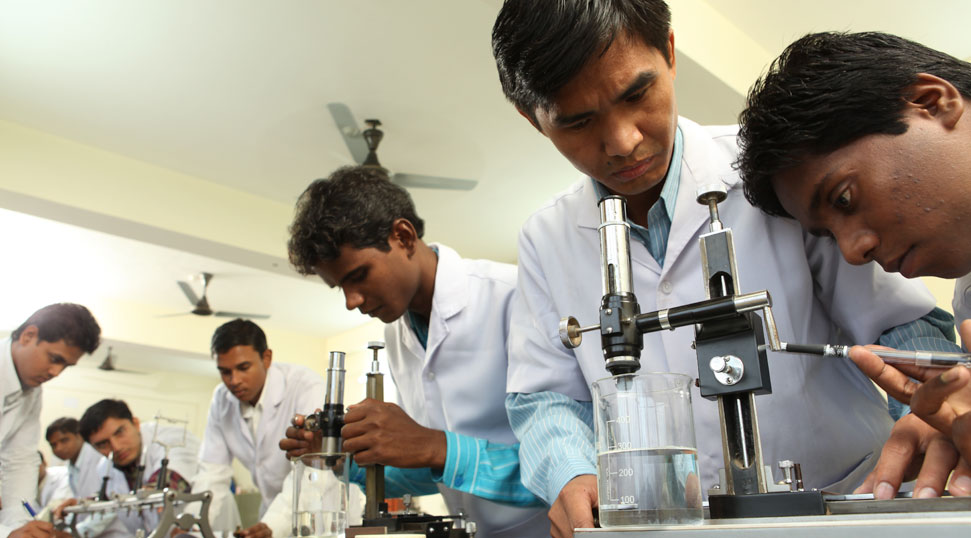

The three-year Bachelor of Science in Medical Imaging Technology programme educates students on the process of taking pictures of human body parts to determine and assess the patient’s condition for clinical evaluations and aims to advance all facets of radiographs. It also includes other medical imaging technology courses, such as those for radiology, ultrasound, nuclear treatment, MRI, dialysis, and other specialities. Students are exposed to lengthy sessions of hands-on instruction under the supervision of seasoned healthcare professionals. This education satisfies the demands of the allied healthcare sector.
Program Education Objective
- To prepare the students with knowledge and skills related to Sectional Anatomy & Terminology, Anatomical relationships/terminology, Anatomy of the upper thorax and mid thorax, Bony structures and muscles, Blood vessels, Lungs, heart and great vessels, Esophagus, Anatomy of the Abdomen, Abdominal blood vessels, Anatomy of the Pelvis- Bony structures and associated muscles, Digestive and urinary systems, Neuro Anatomy, Arterial/venous systems, Basal ganglia, Cranial nerves, Spine, Arterial/venous systems, Muscles, Glands and pharynx, Cable tools and equipments, X-Ray Imaging, Radiological positioning, CT scan, Ultrasound, and MRI.
- This will enable them to apply modern medical imaging tool, techniques, and technologies and also advance their expertise through higher studies and continous learning for practice and applications with ethics and social responsibility.
Career Opportunities
- Medical Advisor,
- Lead Medical Image Analysis Scientist,
- Marketing Executive,
- X-ray Technician,
- Imaging Research Assist. Manager,
- Radiographer,
- Area Sales Manager,
Core Areas
Core Curriculum
Basic Anatomy
Fundamentals of Human Anatomy
Anatomical understanding: cells, tissues, muscles, skeleton, organs, and their structure and function in normal human body.
Tools, Equipment & Safety Measures
Tools Equipment
Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable – Un grounded & Grounded Power Supply Cable, Metallic Sheathed Cable, Multi-Conductor Cable, Coaxial Cable, Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable, Shielded twisted pair cable, Ribbon Cable, Armoured & Unarmoured Cable, Twin-Lead Cable, Twin axial Cable, Optical fiber cable, Connectors,
Radiology
X-ray Imaging
X-ray Tubes – Stationary & Rotation Anode, X-ray Consolestation (Demo of KV, MA and exposure time settings), Procedures to reduce Scattered Radiation, Focus Principle, Grids, Screen, Image intensifiers, Use of contrast materials.
Radiological Positioning
Patient transfer technique – Turning the patient, Restraint techniques – Trauma, Pediatric, Geriatric, physically handicapped, disturbed patients, an aesthetized patient, moving chair & stretcher patients, Tubes & catheters, Nasogastric, chest, Urinary, intravenous, oxygen & other (Castsurgical & cardiac) Alcoholic, bed pans & urinals, Assessment.
CT Scan
Basic Computed Tomography: Basic principles of CT, generations of CT, CT instrumentation, image formation in CT, CT image reconstruction, Hounsfield unit, CT image quality, CT image display, X-ray tube:
Construction working and limitations, generations, methods of cooling the anode, anode rating chart, speed of anode rotation, angle of anode inclination, Focus, anode heel effect, Effect of variation of anode voltage and filament temperature, inherent filter and added filter, bow tie filter, effect on quality of the
spectrum, Collimator designs: Pencil beam, Fan beam, Cone beam CT, Z-axis collimation, detector design – construction and working – Gas filled detectors – solid state detectors – flat panel detectors, Principles of tomography: advantages and limitations – generations – spiral CT –slip ring technology – Multislice CT – dual source CT – pitch – rotation time, Basic principles of Image Reconstruction: Back projection, analytical an iterative methods – MPR – MIP – volume rendering – surface shaded display (SSD) – bone reconstruction, CT artefacts: motion artefacts, streak artefacts, ring artefacts, partial volume artefacts etc. causes and remedy, Dose and Dosimetry: CT Dose Index (CTDI, etc.), Multiple Scan Average Dose (MSAD), Dose Length Product (DLP), Dose Profile, Effective Dose, Phantom Measurement Methods, Dose for Different Application Protocols, Technique Optimization.
Ultrasound
Basic Acoustics, Ultrasound terminologies: acoustic pressure, power, intensity,
impedance, speed, frequency, dB notation: relative acoustic pressure and relative
acoustic intensity.
- Interaction of US with matter: reflection, transmission, scattering, refraction and absorption, attenuation and attenuation coefficients, US machine controls, US focusing.
- Production of ultrasound: Piezoelectricity, Medical ultrasound transducer:
Principle, construction and working, characteristics of US beam. - Ultrasound display modes: A, B, M
MRI
Basic concepts of Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Atomic structure, Hydrogen as imaging medium, magnetism, precession, resonance, Electromagnetic radiation, NMR – basic concepts of MRI, Faraday’s cage, Basic MR Image formation: RF Excitation, Relaxation (T1 and T2), Computation and display, Free induction decay, RF wave form designs.
Introduction to MR coils: Volume coils, Gradient coils, Slice selection, phase encoding, frequency encoding, Artifacts: Cause of artifacts, Image quality, image contrast, signal to noise ratio, resolution, artefacts, MR contrast agents, Advanced MR techniques, flow effects, MR angiography echo planner imaging, magnetization transfer, fat suppression, MR spectroscopy, functional imaging, Magnetic resonance hazards and safety, Recent development, MRI Scanners: Methods of MRI imaging methods, Head and Neck ,Thorax, Abdomen, Musculoskeletal System imaging, Clinical indications and contraindications, types of common sequences effects of sequence on imaging, Protocols for various studies, slice section, patient preparation; positioning of the patient; patient care-calibration -paramagnetic agents and dose, additional techniques and recent advances in MRI; image acquisition-modification of procedures in an unconscious or un co-operative patient, plain studies, contrast studies, special procedures, reconstructions, 3D images, MRS blood flow imaging, diffusion/perfusion scans, strength and limitations of MRI, role of radiographer, MR safety: instrumentation and biological effects
Programme Type - UG
Duration - 3 years
Minimum Eligibility - 10+2 (Science)
Degree Awarded By -